FCA (Free Carrier)
is one of the 11 Incoterms defined in the Incoterms 2020, published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). It is an Incoterm that is commonly used in international trade when the buyer and seller are located in different countries, and the buyer is responsible for arranging and paying for the transportation of the goods.
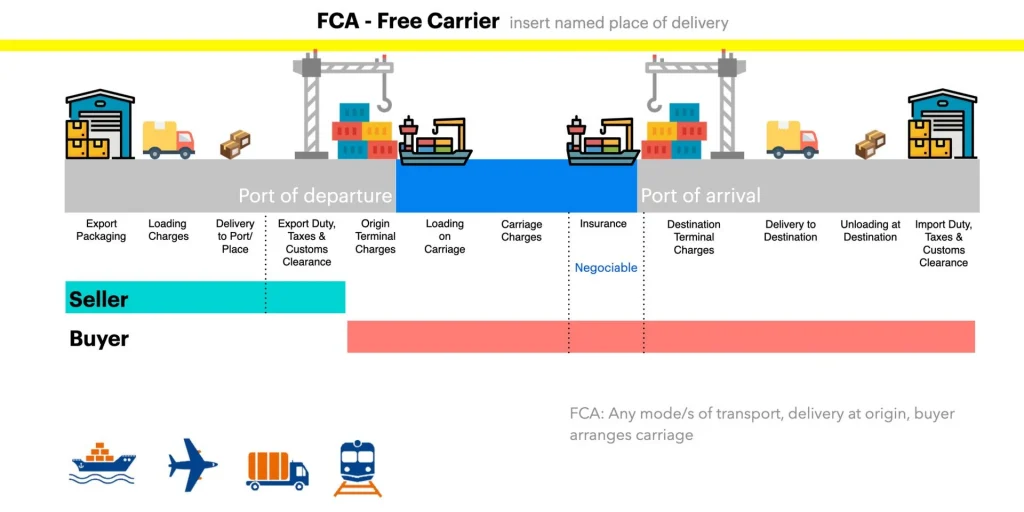
Under FCA, the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the carrier nominated by the buyer at the seller’s premises or another named place. The buyer is responsible for the transportation costs and risks from that point on, including arranging and paying for the transportation, obtaining any necessary export or import licenses and permits, and paying any applicable duties or taxes.
Responsibilities and Obligations of Buyer and Seller
- The seller's responsibilities under FCA include:
- Delivering the goods to the carrier nominated by the buyer at the seller's premises or another named place
- Loading the goods onto the transport vehicle (if agreed upon)
- Obtaining any necessary export licenses or permits
- The buyer's responsibilities under FCA include:
- Arranging and paying for transportation of the goods
- Obtaining any necessary import licenses or permits
- Paying any applicable duties or taxes
- Bearing the risk of loss or damage to the goods once they are delivered to the carrier
Advantages of using FCA include:
- The buyer has more control over the transportation arrangements as they can choose the carrier and mode of transportation
- The buyer can arrange for the goods to be shipped directly to the final destination, avoiding the need for transshipment
- The seller is not responsible for obtaining export licenses or permits
Disadvantages of using FCA include:
- The buyer bears all the risks and costs associated with the transportation of the goods
- The buyer is also responsible for obtaining any necessary licenses or permits and paying any applicable duties or taxes
Examples of when to use FCA include:
- When the buyer has established relationships with carriers and can obtain favorable transportation rates
- When the buyer is importing goods into a country with a well-established customs clearance process and minimal import restrictions
- When the buyer is experienced and well-equipped to handle the transportation arrangements
- When the goods are bulky or heavy and require special handling or equipment to load or unload
It’s important to note that FCA is a more advanced Incoterm than EXW and it shifts some of the responsibilities and risks from the seller to the buyer. It’s important for the buyer to carefully consider their capabilities and resources before choosing to use FCA in a trade agreement, and to consult with legal and logistics experts to ensure compliance with laws and regulations. Additionally, it’s important to agree and specify the exact place of delivery and any other relevant details in the sales contract.
